Blockchain Interoperability Why It Matters for the Future
Blockchain Interoperability: Why It Matters is a pivotal topic that captures the essence of connectivity in the evolving blockchain landscape. With numerous blockchain networks operating independently, the ability for them to communicate and collaborate is becoming increasingly critical. As we dive into this exploration, we’ll uncover the challenges these disparate systems face, the technologies that enable interoperability, and the real-world applications that showcase its significance.
Introduction to Blockchain Interoperability
Blockchain interoperability refers to the ability of different blockchain networks to communicate and interact with one another seamlessly. As the blockchain ecosystem expands, with numerous platforms emerging for various applications, the need for these networks to work together becomes increasingly important. Interoperability facilitates the sharing of data and assets across distinct blockchains, enhancing overall efficiency and unlocking new possibilities for innovation.
Without this capability, the potential of blockchain technology remains fragmented and limited.
The primary challenge facing disparate blockchain networks is their inherent isolation. Each blockchain operates under its own set of protocols and standards, which often leads to incompatible systems. These barriers can hinder collaboration and slow down processes that require data or assets to move across different platforms. Real-world applications have highlighted these interoperability issues. For instance, in the decentralized finance (DeFi) space, users often find it difficult to transfer tokens between Ethereum and Binance Smart Chain due to differences in their underlying technology.
Similarly, projects that aim to utilize multiple blockchain features, such as cross-chain asset transfers, often face significant technical hurdles that prevent them from achieving their full potential.
Challenges of Disparate Blockchain Networks
Interoperability challenges arise from various factors that limit the effective communication between different blockchain networks. Understanding these challenges is crucial for developing solutions that can enhance interoperability within the ecosystem.
- Technical Differences: Each blockchain platform has its own architecture, consensus mechanisms, and data structures, making it difficult to create standardized communication protocols.
- Lack of Standards: The absence of universally accepted standards for blockchain interoperability contributes to the fragmentation of the ecosystem, making integration complex.
- Security Concerns: Facilitating cross-chain interactions can introduce vulnerabilities that compromise the security of both networks involved in the transaction.
- Scalability Issues: As more blockchains attempt to interconnect, the strain on network resources can lead to performance bottlenecks, which can slow down transactions and increase costs.
- Regulatory Challenges: Different jurisdictions may impose varying regulations on blockchain technologies, complicating efforts to create interoperable solutions that comply with legal requirements.
Interoperability is essential for the next phase of blockchain evolution, enabling seamless asset transfer and interaction across different ecosystems.
Real-world examples of these challenges underscore the need for improved interoperability solutions. For instance, projects like Polkadot and Cosmos are specifically designed to address these issues by enabling various blockchains to communicate with one another efficiently, exemplifying the growing recognition of interoperability as a key factor in the future of blockchain technology.
Types of Blockchain Interoperability
Interoperability in blockchain technology can be broadly classified into different types, each serving unique purposes and functionalities. Understanding these types is crucial for recognizing how various blockchains can effectively communicate and work together in a decentralized ecosystem. In this section, we will dive into cross-chain and intra-chain interoperability, along with methods for achieving seamless communication between different blockchain networks.
Cross-Chain Interoperability
Cross-chain interoperability refers to the capability of different blockchain networks to interact and exchange data or value without requiring a centralized intermediary. This type of interoperability is essential for creating a more integrated blockchain ecosystem, allowing for the transfer of assets and information across disparate chains. Methods to achieve cross-chain interoperability include:
1. Atomic Swaps
This technology allows users to exchange cryptocurrencies from different blockchains directly without the need for a trusted third party. It utilizes smart contracts to ensure that if one party fails to deliver the agreed-upon asset, the transaction is voided, which protects both parties.
2. Sidechains
Sidechains are separate blockchains that run in parallel to the main blockchain, allowing for the transfer of assets between them. They enable more complex applications without congesting the main chain.
3. Cross-Chain Bridges
These are protocols that facilitate the transfer of tokens and data between different blockchain networks. They operate by locking assets on one blockchain and minting equivalent assets on another, enabling users to swap between chains seamlessly.
Intra-Chain Interoperability
Intra-chain interoperability, on the other hand, deals with the communication and collaboration between different components within the same blockchain. This can enhance the efficiency and functionality of decentralized applications (dApps) running on a single blockchain.Methods to achieve intra-chain interoperability include:
1. Smart Contracts
Utilizing smart contracts can allow different dApps or modules within a blockchain to interact with one another. This can create more robust applications as different functionalities can be modularized and independently developed.
2. Standardized Protocols
By implementing standardized communication protocols, dApps on the same blockchain can easily share data and interact with each other, leading to a more cohesive ecosystem.
3. Interoperable Tokens
The use of tokens that comply with standards like ERC-20 or ERC-721 can enable seamless transactions and interactions among various dApps on Ethereum, for example.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Interoperability Types
The comparison of cross-chain and intra-chain interoperability highlights their respective strengths and challenges. Below is a table illustrating the advantages and disadvantages of each type.
| Type of Interoperability | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Cross-Chain Interoperability |
|
|
| Intra-Chain Interoperability |
|
|
Benefits of Blockchain Interoperability
Source: 101blockchains.com
Interoperability in blockchain technology holds significant advantages for both developers and users. It facilitates seamless communication and interaction between different blockchain networks, thereby enhancing functionality and expanding use cases. This interconnectedness not only simplifies processes but also drives innovation, ultimately leading to an enriched user experience across decentralized applications (dApps).The benefits of blockchain interoperability are manifold, impacting both the development landscape and the end-user experience.
For developers, it allows for easier integration of various blockchain features and services, reducing the time and complexity involved in building applications. Users, on the other hand, enjoy smoother interactions with multiple blockchain ecosystems, which can lead to enhanced security, reduced costs, and more effective access to decentralized services.
Enhanced Innovation and User Experience
Interoperability acts as a catalyst for innovation, enabling developers to leverage the strengths of multiple blockchain platforms to create more robust and versatile dApps. By connecting diverse ecosystems, developers can implement features that were previously siloed within specific networks. This capability fosters a breeding ground for creative solutions that can address real-world problems.The user experience is significantly improved through interoperability as it allows users to access and utilize services from different blockchains without needing to manage multiple wallets or accounts.
This streamlined approach not only saves time but also minimizes the complexity typically associated with engaging with multiple decentralized platforms. Examples of projects that have successfully embraced interoperability include:
- Polkadot: This multi-chain framework allows distinct blockchains to communicate and share information, enabling developers to create specialized blockchains that can benefit from the security and interoperability of the entire network.
- Cosmos: Known as the “Internet of Blockchains,” Cosmos facilitates communication between various independent blockchains through its Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol, allowing for the transfer of tokens and data seamlessly across networks.
- Chainlink: While primarily a decentralized oracle network, Chainlink enables smart contracts on various blockchains to securely interact with real-world data, APIs, and payment systems, showcasing interoperability in action.
By harnessing the power of interoperability, these projects not only achieve their unique objectives but also contribute to the broader blockchain ecosystem’s evolution, proving that collaboration among diverse networks is essential for the future of decentralized technology.
Technologies Enabling Interoperability
In the dynamic landscape of blockchain technology, interoperability stands out as a crucial aspect that enhances collaboration across various networks. Several technologies have emerged to facilitate this integration, ensuring that different blockchains can communicate and interact seamlessly. Understanding these technologies provides insight into how they contribute to a more cohesive ecosystem that benefits users and developers alike.
Sidechains and Their Role
Sidechains are independent blockchains that run parallel to a main blockchain, allowing assets to be transferred between them securely. This mechanism enhances interoperability by enabling the main blockchain to offload transactions or functionalities to the sidechain, which can operate under different protocols or consensus mechanisms. This capability not only increases scalability but also allows for experimentation with new features without jeopardizing the security of the primary chain.
“Sidechains enable the primary blockchain to extend its capabilities while maintaining its integrity.”
The use of sidechains can significantly improve transaction speeds and reduce costs for users, as they can leverage less congested networks for specific operations. For instance, the Liquid Network is a well-known example of a sidechain that facilitates faster Bitcoin transactions, showcasing how sidechains can streamline operations while preserving the value of the mainchain’s security features.
Oracles and Data Connectivity
Oracles serve as bridges between blockchains and the external world, providing real-time data from outside sources. This technology plays a vital role in enhancing interoperability by allowing smart contracts on one blockchain to access data generated on another blockchain or even off-chain. By delivering accurate and reliable data, oracles enable various blockchain applications to function effectively across different networks.
“Oracles empower blockchains to interact with real-world data, breaking the isolation of chains.”
For example, Chainlink is a widely used decentralized oracle network that allows blockchain applications to securely connect with external data sources, APIs, and payment systems. This functionality is crucial for applications such as decentralized finance (DeFi), where accurate pricing or event data is essential for contract execution.
Bridges Facilitating Asset Transfers
Bridges are critical technologies that facilitate the transfer of assets between different blockchains. They work by locking assets on one chain and minting equivalent tokens on another, enabling users to move value across ecosystems seamlessly. This process not only enhances liquidity but also allows users to participate in various decentralized applications (dApps) without being restricted to a single blockchain platform.
“Bridges expand the usability of assets across multiple blockchain environments, enhancing user experience.”
An example of a well-known bridge is the Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC), which allows Bitcoin to be used within the Ethereum ecosystem. Such innovations allow users to leverage the benefits of both blockchains, driving further adoption and creating a more interconnected blockchain landscape.
Layer 2 Solutions Enhancing Interoperability
Layer 2 solutions are designed to improve blockchain scalability and speed by processing transactions off the main chain while still leveraging its security. These solutions are critical for interoperability as they allow different Layer 1 blockchains to communicate effectively without being burdened by their respective limitations.Layer 2 networks like Lightning Network for Bitcoin and Optimistic Rollups for Ethereum exemplify how these solutions can facilitate faster transactions and lower fees while enabling cross-chain interactions.
By reducing the load on the main blockchain, Layer 2 solutions help create an environment where various blockchain networks can engage with one another more fluidly.
“Layer 2 solutions create a scalable framework that supports interoperability between different blockchain networks.”
In summary, the combination of sidechains, oracles, bridges, and Layer 2 solutions forms a robust technological foundation that enhances blockchain interoperability. These technologies collectively enable a rich ecosystem of interconnected blockchains, allowing users to benefit from greater flexibility, speed, and functionality across diverse platforms.
Real-world Applications of Blockchain Interoperability
Blockchain interoperability is a game-changer across various industries, enabling seamless communication between different blockchain networks. As organizations increasingly recognize the potential of interoperable systems, many sectors are leveraging this technology to enhance efficiency, transparency, and security. Interoperability plays a crucial role in several industries, particularly in finance, supply chain, and healthcare. By allowing disparate blockchain networks to communicate and share data, businesses can streamline operations, reduce costs, and open new avenues for innovation.
Below are some notable sectors capitalizing on blockchain interoperability, along with successful case studies and impactful statistics.
Finance Industry
The finance sector is one of the most significant beneficiaries of blockchain interoperability. Financial institutions are increasingly utilizing interoperable blockchains to improve transaction efficiency and facilitate cross-border payments. A standout example is Ripple, which uses its platform to enable real-time, cross-border transactions between different fiat currencies. According to a report by the World Economic Forum, it is estimated that 10% of global GDP will be stored on blockchain technology by 2027, emphasizing the potential impact of interoperability on financial systems.
Additionally, banks can reduce transaction costs by up to 60% through blockchain solutions.
Supply Chain Management
Interoperability is revolutionizing supply chain management by enhancing traceability, accountability, and efficiency. IBM’s Food Trust uses blockchain to connect various entities within the food supply chain, from farms to retailers. This ensures that all participants can access and verify data related to food safety, provenance, and quality. In a case study involving Walmart, the company reported a reduction of food traceability time from days to mere seconds due to blockchain implementation.
This not only increases consumer trust but also helps in quickly identifying and isolating foodborne illness outbreaks, thereby saving costs and protecting public health.
Healthcare Sector
The healthcare industry is also witnessing significant advancements through blockchain interoperability. By linking different healthcare systems, patient data can be securely shared between providers while maintaining privacy and compliance with regulations. Projects like MedRec, developed by MIT, demonstrate how blockchain can facilitate data sharing among hospitals and doctors, enabling better patient care.A study by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) highlighted that blockchain could reduce healthcare administrative costs by as much as $150 billion annually through improved data interoperability and reduced fraud.
“Blockchain interoperability represents a leap towards a more connected and efficient digital economy.”
The successful implementation of interoperable blockchain solutions across these sectors showcases the transformative potential of this technology. As industries continue to adopt blockchain, the ability to communicate across networks will be paramount in driving progress and innovation.
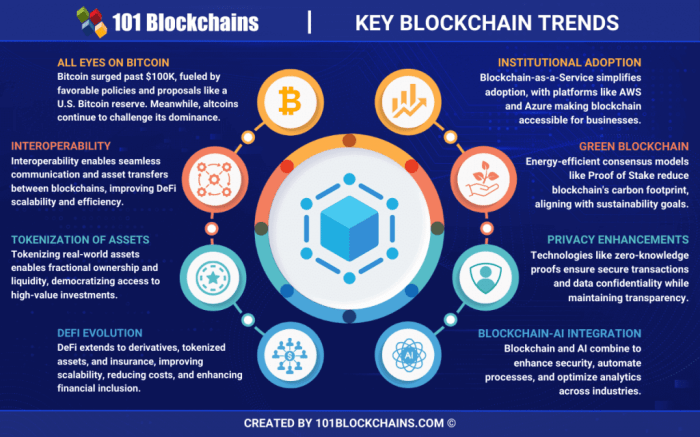
Future Trends in Blockchain Interoperability

Source: shortpixel.ai
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, the importance of interoperability becomes increasingly critical. The future of blockchain interoperability is likely to be shaped by several emerging trends and innovations. These developments not only promise to enhance the functionality of individual blockchains but also to create a more cohesive ecosystem where different blockchain networks can communicate and transact seamlessly. In this segment, we will explore the anticipated trends that will drive interoperability forward, including the influence of regulatory frameworks and emerging technologies, as well as provide a glimpse into the future with a table outlining predicted advancements.
Emerging Trends and Innovations
Several trends are on the horizon that could significantly impact how blockchain interoperability develops. One prominent trend is the advancement of cross-chain communication protocols, which aim to facilitate interactions between disparate blockchains. Innovations such as atomic swaps and decentralized exchange protocols are leading the charge, allowing users to trade assets across different chains without the need for intermediaries.Another trend is the increasing focus on standardization.
As more organizations recognize the need for unified communication standards, initiatives are being launched to create regulatory frameworks that support interoperability. These frameworks are essential as they encourage collaboration among blockchain developers and stakeholders, ultimately leading to a more interconnected blockchain landscape.
Role of Regulatory Frameworks and Standards
Regulatory frameworks play a pivotal role in fostering blockchain interoperability by establishing guidelines that ensure compliance and security. The establishment of standardized protocols reduces fragmentation within the blockchain ecosystem, making it easier for different networks to interoperate. For instance, the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) has initiated discussions regarding blockchain standards aimed at enhancing interoperability across various platforms. These standards help mitigate risks associated with cross-chain transactions and ensure that user data remains secure, thus promoting trust in blockchain applications.
Predicted Advancements in Interoperability Technologies, Blockchain Interoperability: Why It Matters
The next five years are expected to witness significant advancements in blockchain interoperability technologies. These advancements will drive the development of more robust cross-chain solutions. The table below highlights some key predicted developments in this space:
| Year | Advancement | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | Enhanced Cross-Chain Protocols | Development of more efficient protocols to facilitate instant asset transfers between blockchains. |
| 2025 | Standardized Interoperability Frameworks | Implementation of industry-wide standards for blockchain communication, improving compatibility. |
| 2026 | Interoperability Layer Solutions | Emergence of dedicated interoperability layers that connect multiple blockchains seamlessly. |
| 2027 | Decentralized Identity Solutions | Integration of decentralized identity systems that enhance user privacy and secure cross-chain interactions. |
| 2028 | AI-Driven Interoperability | Incorporation of AI technologies to optimize blockchain connections and automate cross-chain transactions. |
As the blockchain landscape evolves, interoperability will be at the forefront of innovation, enabling a more connected and efficient digital economy.
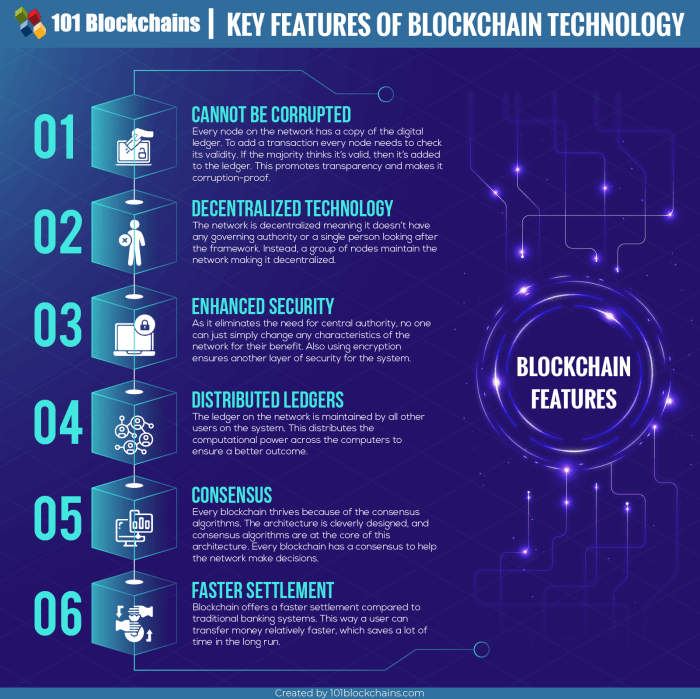
Challenges and Limitations
Source: 101blockchains.com
The journey towards achieving seamless blockchain interoperability is riddled with various challenges and limitations. While the potential benefits are clear, several technical and regulatory hurdles must be overcome to facilitate broader adoption of interoperability solutions. It’s essential to understand these barriers as they play a significant role in shaping the landscape of blockchain technology.
Technical and Regulatory Challenges
Interoperability solutions face significant technical challenges. These include differences in consensus mechanisms, data formats, and transaction protocols across various blockchain platforms. Each blockchain has its unique architecture, which complicates the development of universal standards for data exchange. Additionally, varying levels of scalability and transaction speed among networks can hinder effective communication between them. On the regulatory front, the lack of standardized regulations governing blockchain technology creates uncertainty for developers and businesses.
Different jurisdictions may impose conflicting requirements, making it challenging for companies to navigate compliance. This regulatory ambiguity can slow down innovation and discourage investment in interoperability solutions.
Security Risks and Mitigation Strategies
Interoperable systems are not without their security risks. The increased complexity of connecting multiple blockchains can provide more entry points for potential attacks. For instance, a vulnerability in one blockchain could potentially compromise the entire network of interconnected blockchains. Moreover, smart contracts that facilitate interoperability might have coding flaws resulting in exploitation.To mitigate these risks, developers can implement various security strategies.
Regular audits of smart contracts are crucial to identify and rectify potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Utilizing multi-signature wallets and decentralized identity solutions can enhance security by ensuring that transactions are authorized by multiple parties before execution. Establishing clear protocols for data exchange can also help in protecting sensitive information and maintaining the integrity of transactions.
Overcoming Limitations in Development
Developers play a critical role in addressing the limitations of blockchain interoperability. Emphasizing collaboration among developers from various blockchain ecosystems fosters a culture of innovation and shared learning. Creating open-source frameworks for interoperability can also accelerate development, as they allow for collective troubleshooting and improvement.Incorporating modular designs can enhance adaptability, enabling developers to create solutions that can easily integrate with different blockchains while minimizing the effort required for adaptation.
Additionally, investing in interoperability protocols, such as Polkadot or Cosmos, which are specifically designed to facilitate cross-chain interactions, can significantly streamline the process.
Community and Ecosystem Initiatives: Blockchain Interoperability: Why It Matters
Community initiatives and organizations play a crucial role in fostering blockchain interoperability. By collaborating across various sectors, these groups seek to break down the silos that often hinder blockchain technologies from working together seamlessly. As the landscape of blockchain evolves, the need for interconnected systems becomes increasingly apparent, driving the formation of alliances aimed at solving interoperability challenges.One notable aspect of these initiatives is the formation of consortiums and partnerships that focus specifically on the development of interoperable blockchain solutions.
These collective efforts bring together stakeholders from different industries, including technology, finance, healthcare, and supply chain, to share knowledge, resources, and best practices. Such collaboration not only accelerates innovation but also establishes standards that promote compatibility among diverse blockchain networks.
Consortiums and Partnerships Promoting Interoperability
Numerous consortiums and partnerships have emerged to tackle the interoperability issue head-on, reflecting the collaborative spirit of the blockchain community. Some of these key initiatives include:
- InterWork Alliance: This consortium aims to create a framework for the interoperability of smart contracts across different platforms, enabling businesses to leverage the benefits of blockchain technology without being locked into a single network.
- Enterprise Ethereum Alliance (EEA): The EEA focuses on establishing standards for Ethereum-based blockchain applications. By promoting shared technical standards, the EEA helps various enterprises to build interoperable solutions that can communicate with each other seamlessly.
- Hyperledger Project: Under the umbrella of the Linux Foundation, Hyperledger is a global collaboration encouraging the development of open-source blockchain technologies. It includes various working groups focused on interoperability among blockchain implementations.
- Polkadot: This platform is designed specifically to enable different blockchains to transfer messages and value in a trust-free fashion. Polkadot’s unique architecture facilitates interoperability by allowing distinct blockchains to maintain their sovereignty while being able to communicate with one another.
- Blockchain Interoperability Alliance: This organization promotes the integration of blockchain technologies and supports the development of standards and protocols that facilitate interoperability among different blockchain networks.
These initiatives address various interoperability challenges by focusing on standardization, shared protocols, and collaborative development. They engage in research and development to create tools that simplify cross-chain communication and enhance compatibility.
“Interoperability is not just a technical challenge; it’s about creating a collaborative ecosystem where different blockchain networks can coexist and function together.”
In summary, community and ecosystem initiatives are pivotal in advancing blockchain interoperability. Through collective action and shared goals, these organizations strive to create an interconnected blockchain landscape that can support diverse applications and foster innovation across industries.
Last Word
In conclusion, understanding Blockchain Interoperability: Why It Matters is essential for anyone looking to grasp the future of decentralized technologies. The benefits of seamless integration among various blockchain networks not only enhance user experience but also foster innovation across multiple industries. As we look ahead, the continued development of interoperability solutions promises to unlock new possibilities and create a more interconnected blockchain ecosystem.
Questions Often Asked
What is blockchain interoperability?
Blockchain interoperability refers to the capability of different blockchain networks to communicate and share data with one another.
Why is interoperability important?
Interoperability is crucial as it allows for greater collaboration among different blockchain systems, enhancing their functionality and utility.
What are some challenges to achieving interoperability?
Challenges include technical limitations, lack of standardized protocols, and regulatory issues that hinder seamless integration.
How can interoperability benefit developers?
For developers, interoperability can lead to enhanced application features, access to a broader user base, and the ability to create more advanced solutions.
What industries can benefit from blockchain interoperability?
Industries such as finance, supply chain, healthcare, and more can significantly benefit from improved data sharing and operational efficiency through interoperability.