How Blockchain Is Transforming Global Finance Today
How Blockchain Is Transforming Global Finance is a revolutionary exploration into how this innovative technology reshapes the very foundations of financial systems. With its core principles rooted in decentralization and security, blockchain offers unprecedented opportunities to enhance transparency and efficiency in financial transactions. As we delve into its evolution, we uncover the significance of blockchain in redefining traditional banking and paving the way for a more inclusive financial landscape.
This transformation extends to emerging financial products, regulatory challenges, and the future trends poised to influence global markets. The impact of blockchain is not merely theoretical; it is actively changing the way we think about money, transactions, and trust in financial interactions.
Introduction to Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has emerged as a groundbreaking innovation, particularly in the financial sector, where it promises to transform how transactions are conducted. At its core, blockchain is a distributed ledger system that ensures transparency, security, and efficiency in recording transactions. This digital ledger is immutable and decentralized, meaning that it does not rely on a central authority to validate transactions.
Instead, it utilizes a network of computers (nodes) that maintain copies of the ledger, allowing for a consensus mechanism that verifies each transaction.The history of blockchain technology dates back to 2008 when an individual or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto introduced it as the foundational technology behind Bitcoin. This marked the beginning of a new financial paradigm that challenged traditional banking systems.
Over the years, blockchain has evolved significantly, transitioning from a mere cryptocurrency platform to a versatile tool that supports various applications in finance, such as smart contracts, decentralized finance (DeFi), and tokenization of assets. Its ability to reduce costs and enhance efficiency has caught the attention of financial institutions worldwide, leading to increased investments and research into its potential.
Fundamental Principles of Blockchain Technology
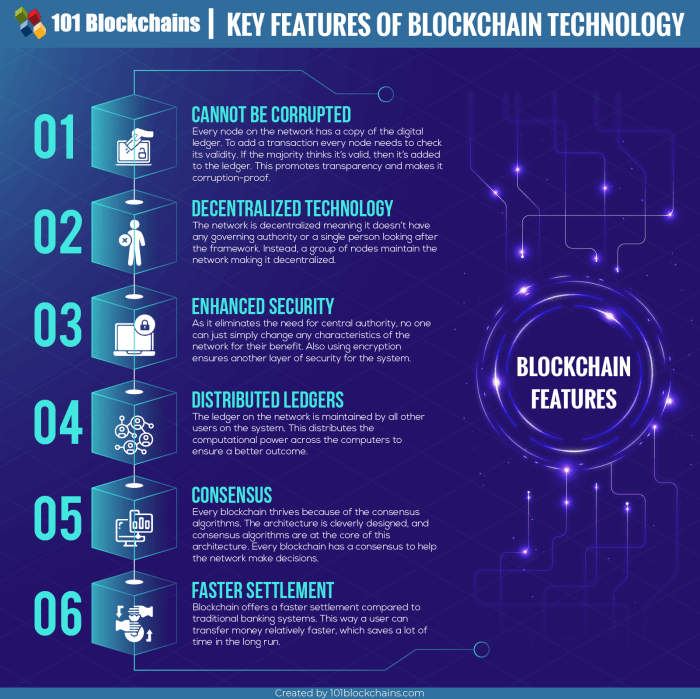
The fundamental principles of blockchain technology are pivotal in understanding its impact on global finance. These principles include decentralization, transparency, immutability, and security.
Decentralization
This principle eliminates the need for a central authority, distributing control across a network of nodes. Each node holds a copy of the entire blockchain, ensuring that no single entity can manipulate or control the data. This is crucial for fostering trust among users.
Transparency
All transactions on a blockchain are visible to participants within the network and are recorded in a way that is tamper-proof. This transparency helps to prevent fraud and enhances accountability.
Immutability
Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This characteristic is achieved through cryptographic hashing, where each block is linked to the previous one. This ensures that the integrity of the data is maintained over time.
Security
Blockchain employs advanced cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and protect user identities. This security framework makes it nearly impossible for malicious actors to alter transaction records or compromise the network.
“Blockchain technology is disrupting traditional finance by providing a secure, efficient, and transparent way to conduct transactions.”
The importance of decentralization in finance cannot be overstated. It fosters an environment where individuals and businesses can transact without intermediaries, thereby reducing costs and increasing the speed of transactions. This shift towards decentralized finance (DeFi) has led to the creation of various financial products and services that operate outside of traditional banking systems, empowering users with greater control over their financial assets.
Through these principles, blockchain technology is laying the groundwork for a more inclusive and efficient global financial ecosystem.
Key Features of Blockchain in Finance
Blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary force in the financial sector, providing a range of features that cater to the complex needs of modern finance. These features facilitate secure transactions, enhance transparency, and streamline processes across various financial applications. Understanding these key attributes is crucial for grasping how blockchain can alter the landscape of global finance.One of the standout features of blockchain technology is its decentralization, which eliminates the need for intermediaries in financial transactions.
This characteristic significantly reduces transaction costs and time delays, making processes faster and more efficient. Moreover, the distributed ledger technology ensures that all participants in the network have access to the same data, thereby enhancing trust among parties involved in transactions.
Role of Transparency and Security in Blockchain Transactions
The importance of transparency and security in financial transactions cannot be overstated. Blockchain offers a level of transparency that traditional financial systems struggle to achieve. Each transaction is recorded on a public ledger, accessible to all network participants. This openness promotes accountability and enables participants to verify transactions independently.Security in blockchain transactions is achieved through cryptographic techniques that secure data and prevent unauthorized access.
Each block in the chain is linked to the previous block using hash functions, creating a secure and tamper-proof chain of information. By utilizing public and private keys, blockchain ensures that only authorized users can initiate transactions, protecting sensitive financial information.
“The decentralized nature of blockchain means that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted, fostering a secure environment for financial transactions.”
Significance of Immutability in Financial Data Management
Immutability is one of the cornerstone features of blockchain technology, particularly in financial data management. Once data is entered into the blockchain, it cannot be modified or deleted, which preserves the integrity of the information. This characteristic is vital for financial institutions where data accuracy and reliability are paramount.The immutability of blockchain leads to enhanced trust among users, as they can be confident that the data they are accessing has not been tampered with.
This is especially critical in areas such as auditing and compliance, where maintaining an accurate historical record is essential. For instance, financial institutions can utilize blockchain to create an immutable audit trail that provides transparency and accountability in all transactions.In summary, the key features of blockchain, including transparency, security, and immutability, position it as a transformative technology in the finance sector.
These attributes not only streamline processes but also enhance trust, making blockchain an attractive solution for various financial applications.
Impact on Traditional Banking Systems
The advent of blockchain technology is reshaping the landscape of global finance, particularly by challenging the traditional banking systems that have long been the backbone of financial transactions. Traditional banks have operated with a centralized model, which often comes with inefficiencies and higher costs. In contrast, blockchain presents a decentralized approach that offers significant advantages in terms of operation, transparency, and security.Blockchain significantly reduces the need for intermediaries in financial transactions, such as banks and payment processors.
By utilizing smart contracts and decentralized ledgers, individuals and organizations can engage in direct transactions without relying on a third party to validate or facilitate the exchange. This not only streamlines the transaction process but also minimizes costs associated with intermediaries, such as fees and processing times.
Reduction of Intermediaries in Financial Transactions
The reliance on intermediaries has been a hallmark of traditional banking systems; however, blockchain technology aims to change that dynamic. By leveraging its distributed ledger capabilities, blockchain enables peer-to-peer transactions that enhance efficiency. Key points regarding this transformation include:
- The elimination of manual processes often associated with traditional banking, leading to faster transaction times.
- Reduction of operational costs, since users do not incur charges from intermediaries.
- Increased transparency, as all transactions are recorded on a public ledger that can be accessed by all parties involved.
- Improved security measures, leveraging cryptographic techniques to protect against fraud and unauthorized access.
Enhancement of Cross-Border Payment Efficiency
Cross-border payments have traditionally been characterized by high fees, lengthy processing times, and a lack of transparency. Blockchain technology addresses these issues by providing a more efficient and cost-effective solution. When analyzing its impact, several aspects stand out:
- Instantaneous transactions allow for real-time processing without the typical delays associated with international banks.
- Lower transaction fees compared to conventional methods such as wire transfers, which can charge hefty fees for cross-border transactions.
- Access to a global network of users, enabling businesses to transact with international clients without worrying about currency conversion fees or exchange rate fluctuations.
- Enhanced traceability of funds, allowing parties to track the movement of their money across borders seamlessly.
“Blockchain technology not only streamlines cross-border transactions but also empowers users with unprecedented control over their financial assets.”
Emerging Financial Products and Services
The advent of blockchain technology has catalyzed a wave of innovative financial products and services that are reshaping the landscape of global finance. These emerging solutions leverage the unique features of blockchain to offer enhanced security, transparency, and efficiency, ultimately benefiting consumers and businesses alike. As the technology matures, we see a diversification in financial offerings that challenge traditional paradigms.One significant area influenced by blockchain is the creation of new financial products tailored to meet evolving consumer demands.
These innovations include:
- Cryptocurrency Loans: Platforms facilitating cryptocurrency-backed loans allow users to leverage their digital assets without needing to liquidate them.
- Tokenized Assets: Real-world assets such as real estate and art can now be represented as tokens on a blockchain, simplifying ownership transfers and fractional investments.
- Decentralized Insurance: Insurance products that use blockchain to automate claims processing and risk assessment through transparent data sharing.
- Stablecoins: Digital currencies pegged to stable assets that provide a reliable means of transaction without the volatility associated with traditional cryptocurrencies.
- Blockchain-based Payment Systems: Innovations in cross-border payment solutions that reduce transaction costs and settlement times.
Smart Contracts in Lending and Insurance Services
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with the terms of the contract directly written into code, stored, and executed on the blockchain. They have revolutionized lending and insurance services by offering a new level of automation and trust.In the lending space, smart contracts enable peer-to-peer lending platforms to operate without intermediaries. By automating verification processes, loan disbursement, and repayment tracking, they eliminate the need for banks as intermediaries, allowing for faster and cheaper transactions.
For example, platforms like Aave and Compound utilize smart contracts to facilitate crypto loans, allowing borrowers to access funds instantly.In insurance, smart contracts streamline claims processing. They can automatically verify claims based on predefined conditions, significantly reducing the time taken to settle claims. For instance, if a flight is delayed, a smart contract can automatically trigger a payout to insured travelers without human intervention, enhancing customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Decentralized Finance Platforms and User Implications
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) platforms represent a major shift in how financial services are delivered, removing traditional intermediaries such as banks and brokers. DeFi allows users to lend, borrow, trade, and earn interest on their assets directly through blockchain technology.These platforms come with several implications for users:
Accessibility
DeFi platforms are open to anyone with an internet connection, removing barriers associated with traditional banking systems. This inclusivity empowers a wider audience to engage in financial activities.
Control
Users maintain control of their assets and transactions, as they interact directly with smart contracts rather than relying on a centralized authority.
Yield Farming and Liquidity Mining
DeFi users can often earn higher returns on their investments through yield farming or liquidity mining, incentivizing participation in various financial services.
Risks
While DeFi offers innovative solutions, it also comes with risks such as smart contract vulnerabilities and regulatory uncertainties. Users must be cautious and conduct thorough research before engaging with these platforms.Overall, the emergence of blockchain-powered financial products and services is paving the way for a more inclusive, efficient, and transparent financial ecosystem. As technology continues to evolve, the possibilities for innovation in finance are boundless.
Regulatory Challenges and Considerations

Source: blueoceanacademy.com
The regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain technology in global finance is evolving rapidly. As blockchain continues to gain traction, regulators are tasked with formulating frameworks that ensure the technology’s security and transparency while fostering innovation. This presents a balancing act between maintaining financial stability and encouraging the growth of blockchain solutions.Regulators face several challenges in adapting to blockchain technology, primarily due to its decentralized nature and the speed at which it evolves.
Traditional regulatory frameworks often struggle to keep pace, leading to gaps in oversight. Key challenges include the identification of responsible parties, the potential for cross-border regulatory discrepancies, and the need for comprehensive consumer protection.
Challenges Faced by Regulators
The adaptation of existing regulatory frameworks to accommodate blockchain technology is fraught with difficulties. These challenges necessitate a thorough understanding and addressing of the following aspects:
- Decentralization: The lack of central control complicates the identification of accountable entities, making enforcement more challenging.
- Cross-Border Transactions: Blockchain’s global reach creates jurisdictional issues, leading to potential regulatory arbitrage.
- Rapid Technological Change: The speed at which blockchain technology evolves often outstrips the ability of regulators to respond effectively.
- Data Privacy and Security: Ensuring compliance with evolving data protection regulations is vital, as blockchain’s transparency can conflict with privacy requirements.
“The decentralized nature of blockchain presents unique regulatory challenges that traditional financial systems do not encounter.”
Compliance Measures for Blockchain Solutions
For blockchain solutions to thrive in a regulated environment, robust compliance measures must be integrated into their design. These measures are essential for addressing regulatory expectations and ensuring consumer protection:
- KYC (Know Your Customer): Implementing rigorous identity verification processes to comply with anti-money laundering (AML) regulations.
- Transaction Monitoring: Creating systems that can monitor and flag suspicious activities, ensuring adherence to regulatory standards.
- Data Encryption: Utilizing advanced encryption techniques to protect user data while maintaining compliance with privacy laws.
- Smart Contract Audits: Regular audits of smart contracts to ensure they operate as intended and comply with applicable regulations.
By proactively addressing these compliance measures, blockchain solutions can navigate complex regulatory environments and contribute to the stability and integrity of the global financial system.
Future Trends in Blockchain and Finance
The integration of blockchain within financial markets is set to revolutionize how transactions are executed, offering unprecedented transparency, security, and efficiency. As the technology matures, we can anticipate various trends that will not only reshape existing financial systems but also pave the way for innovative products and services. This segment explores these future trends, particularly the potential for blockchain to enhance global financial inclusion and the role of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) in transforming the finance sector.
Integration of Blockchain in Financial Markets, How Blockchain Is Transforming Global Finance
The adoption of blockchain technology in financial markets is projected to grow significantly, driven by its ability to streamline processes and reduce costs. Financial institutions are increasingly exploring decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, which enable direct transactions between parties without traditional intermediaries, fostering a more efficient financial ecosystem. Key trends include:
- Increased use of smart contracts for automating transactions and facilitating complex agreements without the need for third parties.
- Rise of tokenized assets, allowing for fractional ownership and enhanced liquidity in various asset classes, including real estate and art.
- Greater interoperability among different blockchains, enabling seamless transactions across various platforms, which will encourage wider adoption.
As these trends materialize, blockchain will not only enhance transaction efficiency but also reduce the risks associated with traditional payment systems.
Enhancement of Financial Inclusion Globally
Blockchain technology holds significant potential to enhance financial inclusion by providing access to financial services for underbanked and unbanked populations worldwide. The decentralized nature of blockchain removes barriers that often restrict access to traditional banking systems, such as geographic constraints and high fees.The implications of this trend are profound:
- Microfinance solutions leveraging blockchain can offer low-cost loans to individuals who lack access to traditional banking services.
- Digital wallets powered by blockchain can enable peer-to-peer transactions, allowing users to send and receive money without incurring hefty fees.
- Identity verification solutions on the blockchain can facilitate access to credit and insurance for individuals lacking formal identification.
By breaking down these barriers, blockchain is poised to empower millions, contributing to economic growth and stability in developing regions.
Implications of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
The emergence of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) represents a significant evolutionary step in the finance sector. CBDCs leverage blockchain technology to create digital forms of fiat currency, offering several advantages over traditional currency systems.The implications of CBDCs include:
- Enhanced monetary policy implementation through direct control over digital currency supply, allowing central banks to respond more effectively to economic fluctuations.
- Improved transaction efficiency by reducing the time and cost associated with cross-border payments, benefiting both consumers and businesses.
- Increased financial stability as CBDCs provide a secure digital alternative to cash, reducing reliance on private payment systems that are prone to disruptions.
As countries like China, Sweden, and the Bahamas pioneer the development of CBDCs, the global finance landscape is likely to undergo transformative changes that challenge existing financial paradigms.
Case Studies of Blockchain Implementation
The application of blockchain technology in the financial sector has ushered in a new era of innovation and efficiency. Several institutions worldwide have successfully integrated blockchain into their operations, leading to improved transparency, reduced costs, and enhanced security. This section explores notable case studies of blockchain adoption in finance, showcasing various applications and the lessons learned from both successful implementations and those that fell short.
Successful Blockchain Applications in Finance
Numerous financial institutions have deployed blockchain technology to streamline processes, increase efficiency, and enhance customer experiences. Here are some prominent examples:
- JPMorgan Chase’s Interbank Information Network (IIN): JPMorgan developed the IIN to facilitate cross-border payments and reduce transaction times. By leveraging blockchain, the IIN enables member banks to share information in real-time, significantly mitigating delays caused by the traditional correspondent banking system.
- RippleNet: Ripple’s blockchain-based platform offers a solution for international money transfers. Major banks like Santander and American Express utilize Ripple’s technology to process cross-border payments instantaneously, reducing costs and increasing transaction transparency.
- IBM and Stellar Partnership: IBM’s partnership with Stellar has led to the creation of a blockchain-based cross-border payment solution. The platform enables financial institutions to connect and transact with each other seamlessly, thereby optimizing the global payment process.
- Goldman Sachs’ Digital Asset Group: Goldman Sachs has invested in blockchain technology through its Digital Asset Group. The group explores various applications, including tokenization of assets and blockchain-based trading platforms, demonstrating the bank’s commitment to harnessing blockchain innovations.
Institutions Utilizing Blockchain for Financial Services
Various financial institutions have embraced blockchain to enhance their offerings, leading to improved operational efficiencies and customer satisfaction. Key players include:
- Deutsche Bank: The bank is exploring blockchain for trade finance, aiming to automate and digitize processes that currently rely on paper-based documentation.
- HSBC: HSBC has utilized blockchain for its commodity trade finance operations, enabling quicker settlements and reducing paperwork.
- BNY Mellon: The bank is experimenting with blockchain for asset servicing and has launched a digital asset custody service, reflecting the growing acceptance of cryptocurrencies.
- Visa: Visa is integrating blockchain into its payment system, focusing on enhancing security and efficiency in transactions.
Lessons Learned from Failed Blockchain Projects
While many blockchain initiatives have succeeded, several projects have faced challenges or failed altogether. Understanding these lessons is crucial for future implementations:
- Project Ubin: The Monetary Authority of Singapore initiated Project Ubin to explore the benefits of blockchain in clearing and settlement. The project faced scalability issues when integrating with existing systems, demonstrating the need for careful planning and system compatibility.
- Bank of China’s “Digital Currency Electronic Payment (DCEP): The central bank has faced challenges in the rollout of its digital currency, primarily due to regulatory hurdles and public skepticism about digital currencies.
- Everledger’s Wine Tracking: While Everledger successfully implemented blockchain for tracking fine wines, it struggled with industry adoption due to a lack of consensus among stakeholders on standard practices and data formats.
The key takeaway from failed projects is the importance of aligning technology with business needs and ensuring stakeholder buy-in for successful blockchain adoption.
Conclusion and Outlook
Source: iglu.net
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, its integration into the financial sector promises a transformative impact that will redefine how transactions are conducted globally. The long-term sustainability of blockchain in finance hinges on its ability to foster trust, enhance transparency, and reduce operational costs. These attributes are essential for a financial ecosystem that demands efficiency and reliability in an increasingly digital world.Despite its potential, several barriers could hinder the widespread adoption of blockchain technology in finance.
Key challenges include:
Barriers to Widespread Adoption
Regulatory uncertainties and the complexity of existing financial frameworks pose significant challenges for integrating blockchain solutions. Moreover, the scalability of blockchain networks remains a concern, particularly for institutions managing vast transaction volumes. Here are some additional factors to consider:
- Regulatory Hurdles: The lack of a cohesive regulatory framework across jurisdictions can create confusion and slow down implementation.
- Interoperability Issues: Different blockchain protocols may struggle to communicate with each other, limiting functionality and usability.
- Public Perception: Concerns about security and the association of blockchain with cryptocurrencies can hinder acceptance among traditional financial institutions.
- Technical Challenges: Ensuring cybersecurity and maintaining system integrity in an evolving technological landscape poses ongoing risks.
Looking ahead, the evolution of blockchain in global finance over the next decade appears promising. Financial institutions are increasingly recognizing the necessity of adopting innovative technologies to stay competitive. The following trends are expected to shape the future landscape:
Future Trends in Blockchain and Finance
The future of blockchain in finance will likely be characterized by enhanced collaboration between traditional banks and fintech companies. The proliferation of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms is also expected to drive innovation, creating new financial products that cater to diverse consumer needs.
- Increased Institutional Adoption: Major banks and asset managers are investing in blockchain technology to modernize their operations and improve service offerings.
- Tokenization of Assets: Real-world assets, from real estate to stocks, are being tokenized, allowing for fractional ownership and improved liquidity.
- Smart Contracts: These self-executing contracts will automate processes and reduce the need for intermediaries, thereby streamlining transactions.
- Enhanced Data Security: Utilizing blockchain for secure data management will become increasingly vital, particularly concerning sensitive financial information.
In conclusion, while the path to widespread adoption of blockchain in finance is fraught with challenges, the potential benefits and ongoing advancements suggest a vibrant future. With continuous innovation, regulatory clarity, and a collaborative approach, blockchain is set to play a pivotal role in reshaping the financial landscape for years to come.
Outcome Summary: How Blockchain Is Transforming Global Finance
![Healthcare's Challenges with Blockchain [Webinar] Healthcare's Challenges with Blockchain [Webinar]](https://i1.wp.com/www.creative-tim.com/blog/content/images/2022/10/cover--6-.jpg?w=700)
Source: creative-tim.com
In conclusion, the journey of How Blockchain Is Transforming Global Finance reveals a dynamic intersection of technology and finance, highlighting the potential challenges and opportunities ahead. As we look towards the future, the sustainability and adaptability of blockchain will play a pivotal role in shaping financial innovation. The ongoing evolution signifies a promising horizon where financial systems are not only more efficient but also more accessible to people around the world.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers, ensuring transparency, security, and immutability.
How does blockchain improve financial transactions?
Blockchain improves financial transactions by eliminating intermediaries, reducing costs, enhancing speed, and increasing transparency in the process.
What are smart contracts?
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with the terms directly written into code, enabling automatic enforcement and execution without the need for intermediaries.
What are the regulatory challenges facing blockchain?
Regulatory challenges include compliance with existing laws, ensuring consumer protection, and addressing concerns over security and fraud in blockchain applications.
How might Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) impact global finance?
CBDCs could enhance financial inclusion, streamline payment systems, and provide central banks with greater control over monetary policy and financial stability.